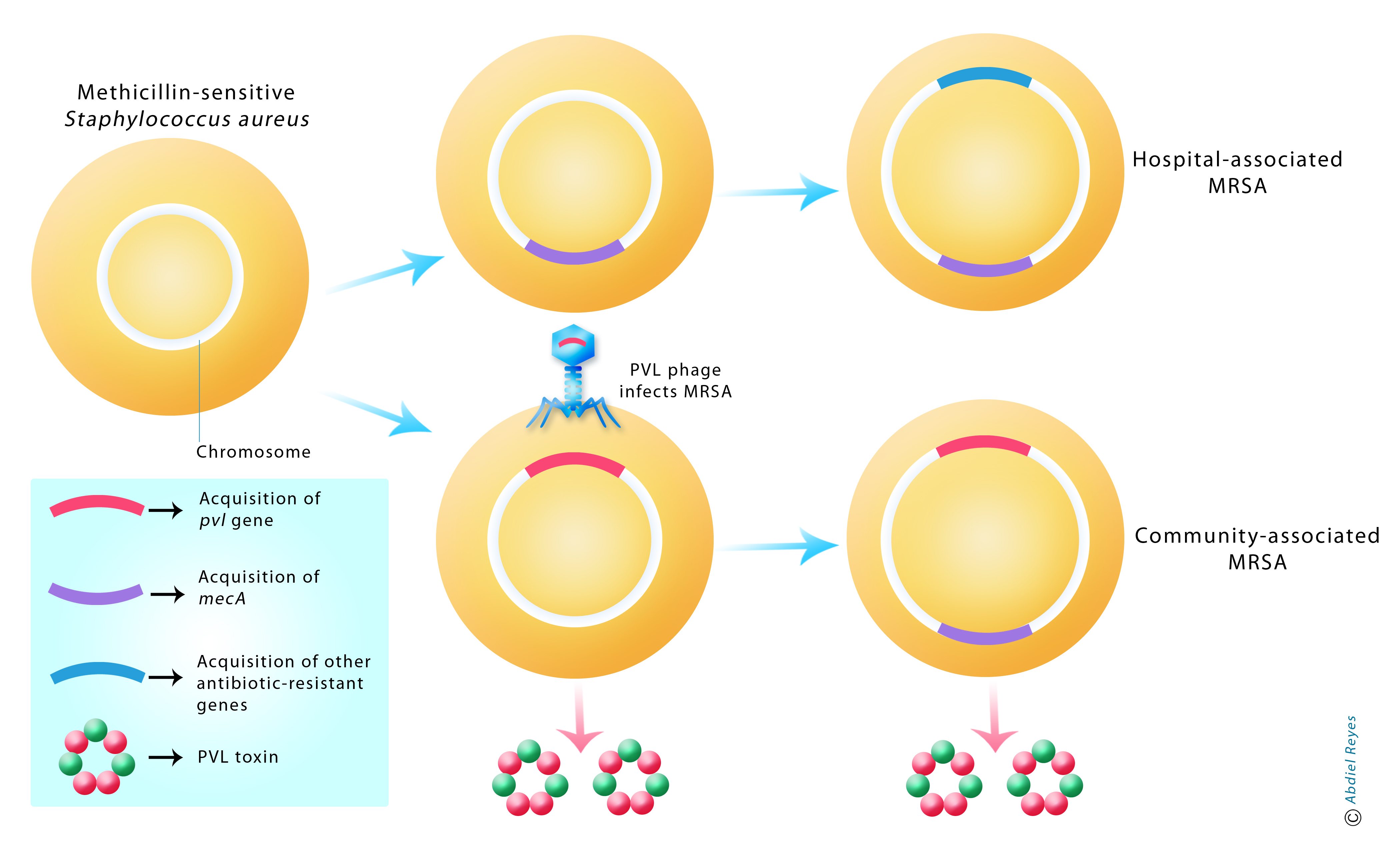
The diagram below illustrates the difference between hospital-associated (HA) and community-associated (CA) MRSA. The methicillin-resistance gene (mecA) can be passed from one bacterial cell to another as a transposable element (a piece of DNA that inserts itself into the bacterial chromosome). The pvl gene is normally present in the genome of the S. aureus bacteriophage and encodes a toxin known as the PVL protein. Upon infection, the phage can insert its DNA into the bacterial chromosome transforming a non-toxic bacterial cell into a bacterium capable of producing the PVL toxin. The mecA gene can be acquired by both CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA. The pvl gene, on the other hand, is found normally in CA-MRSA but not in HA-MRSA.